What Is Overhead Upload And Download
What is network bandwidth?
Network bandwidth is a measurement indicating the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to transmit data over a network connection in a given amount of time. Typically, bandwidth is represented in the number of bits, kilobits, megabits or gigabits that tin exist transmitted in 1 2nd. Synonymous with capacity, bandwidth describes data transfer rate. Bandwidth is not a measure of network speed -- a common misconception.
How does bandwidth work?
The more than bandwidth a data connectedness has, the more than data it tin can transport and receive at in one case. In concept, bandwidth tin can be compared to the book of h2o that can catamenia through a pipe. The wider the pipage's diameter, the more h2o can flow through information technology at 1 time. Bandwidth works on the same principle. The higher the capacity of the communication link, the more than information tin can flow through information technology per second.
The cost of a network connexion goes up every bit bandwidth increases. Thus, a i gigabit per second (Gbps) Dedicated Cyberspace Access (DIA) link will be more expensive than one that can handle 250 megabits per 2nd (Mbps) of throughput.
Bandwidth vs. speed
The terms bandwidth and speed are often used interchangeably only not correctly. The cause of the defoliation may be due, in part, to advertisements by net service providers (ISPs) that conflate the two by referring to greater speeds when they truly mean bandwidth.
Essentially, speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted, while the definition of bandwidth is the capacity for that speed. To employ the water metaphor once more, speed refers to how apace h2o can be pushed through a piping; bandwidth refers to the quantity of h2o that can be moved through the pipage over a set up fourth dimension frame.
Why bandwidth is of import
Bandwidth is not an unlimited resource. In any given deployment location, such every bit a home or business, there is only so much capacity bachelor. Sometimes, this is due to concrete limitations of the network device, such as the router or modem, cabling or wireless frequencies existence used. Other times, bandwidth is intentionally rate-limited by a network administrator or net or wide expanse network (WAN) carrier.
Multiple devices using the same connection must share bandwidth. Some devices, such every bit TVs that stream 4K video, are bandwidth hogs. In comparison, a webinar typically uses far less bandwidth. Although speed and bandwidth are not interchangeable, greater bandwidth is essential to maintain tolerable speeds on multiple devices. To assistance illustrate this, here'south the average bandwidth consumed for various services:

How to measure bandwidth
While bandwidth is traditionally expressed in bits per second (bps), mod network links now accept far greater capacity, which is why bandwidth is at present more than often expressed as Mbps or Gbps.
Bandwidth connections can be symmetrical, which means the data capacity is the same in both directions -- upload and download -- or asymmetrical, which ways download and upload capacity are not equal. In asymmetrical connections, upload capacity is typically smaller than download capacity; this is common in consumer-form internet broadband connections. Enterprise-class WAN and DIA links more than commonly have symmetrical bandwidth.
Considerations for calculating bandwidth
Technology advances have made some bandwidth calculations more than circuitous, and they can depend on the type of network link being used. For example, optical cobweb using different types of light waves and fourth dimension-division multiplexing can transmit more than data through a connexion at one time compared to copper Ethernet alternatives, which effectively increases its bandwidth.
In mobile information networks, such every bit Long-Term Evolution, or LTE, and 5G, bandwidth is defined as the spectrum of frequencies that operators can license from the Federal Communications Commission and the National Telecommunications and Information Administration for use in the U.S. This spectrum cannot exist legally used by anyone other than the business organization that owns the license to information technology. The carrier can then employ wireless technologies to transport data across that spectrum to achieve the greatest bandwidth the hardware tin can provide.
Wi-Fi spectrum, on the other hand, is considered to be unlicensed. Thus, anyone with a Wi-Fi access point (AP) or Wi-Fi router can create a wireless network. The caveat is that the spectrum is not guaranteed to be available. Thus, Wi-Fi bandwidth tin can suffer when there are other Wi-Fi APs attempting to use some or all of the same frequencies.
Effective bandwidth -- which is the highest reliable transmission rate a link can provide on whatever given transport applied science -- can be measured using a bandwidth test. During a bandwidth test, the link'southward chapters is determined past repeatedly measuring the fourth dimension required for a specific file to leave its point of origin and successfully download at its destination.
After determining bandwidth consumption beyond the network, information technology is then necessary to see where applications and data reside and calculate their average bandwidth needs for each user and session.
To understand how much bandwidth a network uplink or internet broadband requires, follow these four steps:
- Determine which applications will be in utilise.
- Determine the bandwidth requirements of each application.
- Multiply the application requirements of each application past the number of expected simultaneous users.
- Add all application bandwidth numbers together.
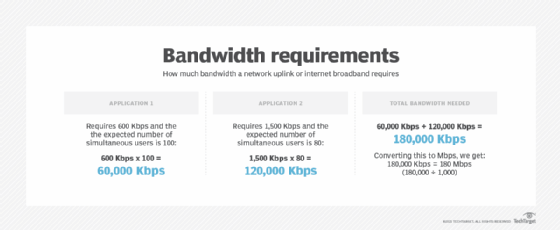
To make up one's mind bandwidth needs for public or individual clouds across cyberspace or WAN links, the aforementioned calculation applies. The difference, withal, is that available bandwidth on a local expanse network or wireless LAN is typically far greater compared to WAN or DIA connections. Thus, accurately assessing bandwidth requirements is critical, every bit is monitoring link utilization over time. Monitoring the corporeality of bandwidth used throughout the twenty-four hours, week, calendar month or year can assistance network engineers make up one's mind whether a WAN/DIA link has sufficient bandwidth -- or if a bandwidth upgrade is needed.
When at that place is insufficient bandwidth on a network, applications and services perform poorly.
Factors affecting network performance
The maximum capacity of a network connection is only one gene that affects network performance. Packet loss, latency and jitter can all degrade network throughput and brand a high-capacity link perform like i with less available bandwidth.
An cease-to-end network path usually consists of multiple connections, each with dissimilar bandwidth capacity. As a result, the link with the lowest bandwidth is often described as the bottleneck considering it can limit the overall capacity of all connections in the path.
Many enterprise-course networks are deployed with multiple aggregated links acting equally a unmarried logical connection. If, for example, a switch uplink uses iv aggregated 1 Gbps connections, it has an constructive throughput capacity of four Gbps. However, if two of those links were to fail, the bandwidth limit would drop to ii Gbps.
Bandwidth on need
Bandwidth for internet or WAN links is typically sold at a set price per month. Nevertheless, bandwidth on demand -- also chosen dynamic bandwidth allotment or burstable bandwidth -- is an culling model that enables subscribers to increase the amount of available bandwidth at specific times or for specific purposes. Bandwidth on demand is a technique that tin can provide additional chapters on a communications link to accommodate bursts in data traffic that temporarily require more than bandwidth.
Rather than overprovisioning the network with expensive dedicated links year-round, bandwidth on demand is often used in WANs to increase capacity equally needed for a special event or fourth dimension of day when traffic is expected to spike. An online flower retailer, for case, may only need to increase its capacity in the weeks leading up to Mother's 24-hour interval. Bandwidth on demand enables enterprises to just pay for the additional bandwidth they eat over a shorter menstruum of time.
Bandwidth on demand is bachelor through many cyberspace and WAN service providers. Depending on the network link a customer currently has in use, a provider may exist able to provision boosted capacity on need using the existing connection. For example, a 100 Mbps link might be able to burst up to 1 Gb because the service provider'due south connection has available capacity. If a customer needed more than the absolute maximum bandwidth bachelor on that link, another physical connectedness would exist required.
Occasionally, a service provider will enable customers to burst above their subscribed bandwidth cap without charging additional fees. However, if customers were to regularly sustain more than 100 Mbps using the burst feature, they are commonly billed by the service provider using 95th percentile calculations.
SD-WAN eases dedicated bandwidth chapters planning processes
Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) technology can provide customers with extra chapters by balancing traffic across multiple WAN and DIA connections rather than a single connexion. SD-WAN deployments frequently apply a Multiprotocol Characterization Switching, or MPLS, connection or other types of dedicated ship links in combination with a lower-cost broadband internet or cellular connection.
How do you optimize and monitor bandwidth employ?
Network engineers have several options available when a network link becomes congested. The most frequent selection is to increase bandwidth. This can be achieved by upgrading the concrete throughput capabilities of the link or through port aggregation and load balancing to logically split traffic across multiple links. Yet, sometimes these techniques are non possible.
ISPs or network administrators may besides intentionally arrange the speed -- up or down -- of data traveling over the network, a measure known as bandwidth throttling. In that location are different reasons for bandwidth throttling, including limiting network congestion, particularly on public admission networks. ISPs may use throttling to reduce bandwidth use by a particular user or class of users. For case, with tiered pricing, a service provider tin can offer a menu of upload and download bandwidth. ISPs can too throttle bandwidth to fifty-fifty out usage across all users on the network.
The use of bandwidth throttling on the cyberspace has been criticized past net neutrality advocates, who say that the exercise can be misused for political or economic reasons and that it unfairly targets segments of the population.
A speed test tin be run to encounter if an ISP is throttling bandwidth. Speed tests measure the speed betwixt a device and a test server using a device's internet connection. ISPs offering speed tests on their own websites, and independent tests are also bachelor from services such equally Speedtest. Considering many factors can affect the results of a speed test, it is by and large recommended to perform multiple tests at different times of the twenty-four hour period and engage different servers bachelor through the speed test site. It is also recommended to acquit a speed test over a wired connectedness.
data transfer throttling intentionally restricts the amount of data sent or received over a network, particularly for the purposes of preventing spam or bulk email transmission through a server. Information technology can be considered some other form of bandwidth throttling. If it is implemented on a large enough scale, information transfer throttling can control the spread of computer viruses, worms or other malware through the cyberspace.
Network bandwidth monitoring tools are available to help identify performance issues, such equally a faulty router or a malware-infected reckoner that is participating in a distributed denial-of-service set on. As noted earlier, bandwidth monitoring can also help network administrators better program for time to come network growth -- seeing where in the network bandwidth is about needed. Monitoring tools can also help administrators see if their ISP is fulfilling the service-level agreement in their contract.
Learn what network chapters planning best practices organizations are putting in place now every bit pandemic concerns brainstorm to subside and more than employees are returning to the role.
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/bandwidth
Posted by: mcculloughaskild.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Overhead Upload And Download"
Post a Comment